Treatment for Hantavirus: Symptoms and Solutions

Effective Treatment for Hantavirus: Symptoms and Solutions
Early treatment for hantavirus can save lives. This article explains how to recognize symptoms, diagnose the infection, and what treatments are most effective.
Key Takeaways
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) is a severe disease primarily transmitted through aerosolized particles from infected rodent droppings, with early symptoms resembling the flu.
Timely diagnosis and treatment are critical for improving survival rates; intensive care, including mechanical ventilation and ECMO, may be necessary in severe cases.
Preventative measures, including rodent control and hygiene practices, coupled with early reporting and diagnosis by healthcare providers, are essential to manage and reduce hantavirus infections.
Understanding Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
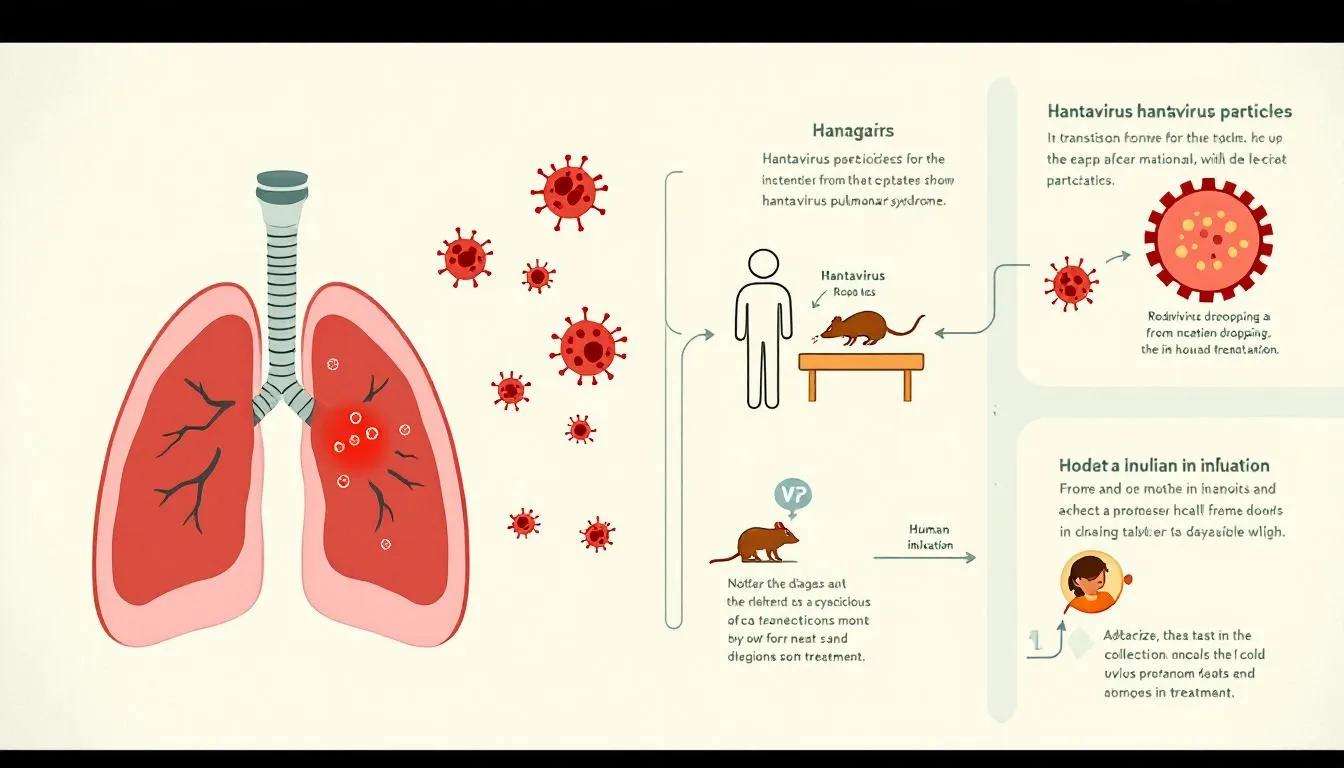
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) is a rare but serious disease caused by viruses, including puumala virus. It can be deadly and primarily impacts the heart and lungs. This severe condition falls under the umbrella of hantavirus infections, which also includes hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS) and infectious diseases. The Sin Nombre virus, commonly found in deer mice, is the principal culprit behind HPS in the United States. Since 1993, there have been 833 recorded cases of HPS in the US, with most cases reported west of the Mississippi River.
Humans contract HPS through exposure to infected rodent droppings, urine, or saliva. The virus is primarily transmitted by breathing in aerosolized particles from rodent excretions. This seemingly innocuous contact can lead to severe health consequences, emphasizing the need to understand HPS infection pathways. Anyone in proximity to infected rodents is at risk of developing HPS.
The symptoms of hantavirus infection initially resemble the flu, with fever, body aches, and fatigue, but can rapidly progress to severe respiratory symptoms. Nearly 40% of HPS cases are fatal, highlighting the disease’s severity and the urgency of early intervention. HPS can escalate quickly, leading to organ failure and death if not treated promptly.
Early treatment significantly improves survival rates. The gravity and rapid progression of hantavirus disease highlight the need for timely medical attention. As we move forward, we will explore the initial symptoms and diagnostic processes that are essential for early detection and successful treatment.
Initial Symptoms and Diagnosis
The early symptoms of hantavirus infection can be deceptive, often mimicking common flu-like symptoms such as fever, body aches, muscle aches, fatigue, and gastrointestinal issues. Recognizing these early symptoms is essential to avoid confusion with other respiratory diseases. The initial stage of hantavirus infection can quickly progress, so paying attention to these signs is critical.
Diagnosis typically involves:
Blood tests, such as the blood test enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which confirm the presence of the virus.
Distinguishing HPS from other diseases with similar symptoms.
Healthcare professionals assessing symptoms.
Confirming rodent exposure.
Using appropriate testing methods.
Early diagnosis and treatment can lead to a complete recovery, even in severe cases of serious disease. Prompt medical advice can prevent progression to an early stage of a more severe disease. As we transition to discussing intensive care management, keep in mind the importance of early detection and intervention in improving patient outcomes.
Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Management
For patients with severe hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, immediate treatment in an intensive care unit (ICU) is often necessary. The critical nature of this disease means that patients may require mechanical ventilation to assist with difficulty breathing. Addressing pulmonary edema, which involves the accumulation of fluid in the lungs, is a key aspect of treatment during the cardiopulmonary phase to prevent respiratory failure.
Effective management involves:
Careful monitoring and control of fluid and volume balance to avoid severe respiratory complications.
Close monitoring and control of blood pressure, which plays a crucial role in supportive care.
Ongoing evaluation and management of renal syndrome, a significant concern.
Without prompt treatment, hantavirus can cause severe trouble breathing and other serious complications. The ICU setting offers the necessary resources and expertise to manage these critical cases. As we explore more advanced treatments like extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), the importance of intensive care becomes even more apparent.
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has emerged as a critical supportive treatment for patients experiencing severe respiratory failure due to hantavirus. Key points about ECMO in this context include:
Venoarterial ECMO (VA-ECMO) is particularly vital in managing severe hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome.
It is especially important for patients exhibiting rapid disease progression.
Early initiation of VA-ECMO can significantly improve survival rates.
Studies show survival rates of up to 80% when VA-ECMO is applied promptly.
Clinical criteria for initiating ECMO in suspected hantavirus cases include a cardiac index below 2.0 L/min per m² and severe hypoxia or refractory shock. These criteria help healthcare providers determine when to employ this life-saving intervention. Patients who received VA-ECMO support for severe hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome showed a survival rate of approximately 66.6%.
Understanding ECMO’s role in treating severe HPS cases underscores the importance of advanced medical interventions in improving patient outcomes. Combining supportive care with targeted treatments offers the best chance for survival.
Antiviral Medications and Their Efficacy
Antiviral medication, particularly intravenous ribavirin, has been explored as potential treatments for hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS). Although ribavirin has shown promise in increasing survival rates in animal studies, it has not significantly reduced mortality rates in humans with HPS. Ribavirin’s antiviral efficacy largely depends on timing, with better outcomes observed when given early in the disease course.
A meta-analysis indicated the following about ribavirin in treating human cases of HPS:
There is a lack of significant clinical benefits from ribavirin.
Timely intervention is critical.
Delayed antiviral treatment is not protective in animal models, emphasizing the importance of early administration.
Combination therapies involving ribavirin may enhance its efficacy compared to its use as a monotherapy.
Despite mixed results, ongoing research into antiviral treatments continues to seek ways to improve outcomes for HPS patients. As we explore supportive care strategies, it becomes clear that a multi-faceted approach is necessary for effective hantavirus pulmonary syndrome treatment.
Supportive Care Strategies
Supportive care is a cornerstone in the management of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. It focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Poor prognosis indicators in hantavirus patients are plasma lactate levels exceeding 4.0 mmol/L. Additionally, a cardiac index below 2.2 L/min/m² is also a concerning sign. Close monitoring of these indicators helps healthcare providers tailor supportive care strategies to individual patient needs.
Effective supportive care can significantly improve patient outcomes by managing symptoms and preventing disease progression and disease control. Exploring experimental treatments and ongoing research offers hope for new and more effective interventions.
Experimental Treatments and Ongoing Research
Experimental treatments and ongoing research are paving the way for more effective treatments. Monoclonal antibodies targeting hantavirus glycoproteins have shown protection in animal models. The development of a standardized polyclonal antibody therapy using hantavirus DNA vaccines is also underway. These innovative approaches aim to bolster the body’s immune response to the virus.
Current clinical trials and treatment strategies for hantavirus include:
Improving the immunogenicity of hantavirus vaccines through innovative delivery methods, such as gene gun inoculation.
Combining antiviral treatments with vaccines to offer a comprehensive strategy against hantavirus infections.
Repurposing FDA-approved drugs that target vasoactive mediators as a novel approach to treating hantavirus infection.
These experimental treatments and ongoing research efforts offer hope for more effective future interventions. As we discuss prevention strategies, it becomes clear that a multi-pronged approach is essential to combat hantavirus infections effectively.
Prevention of Hantavirus Infections
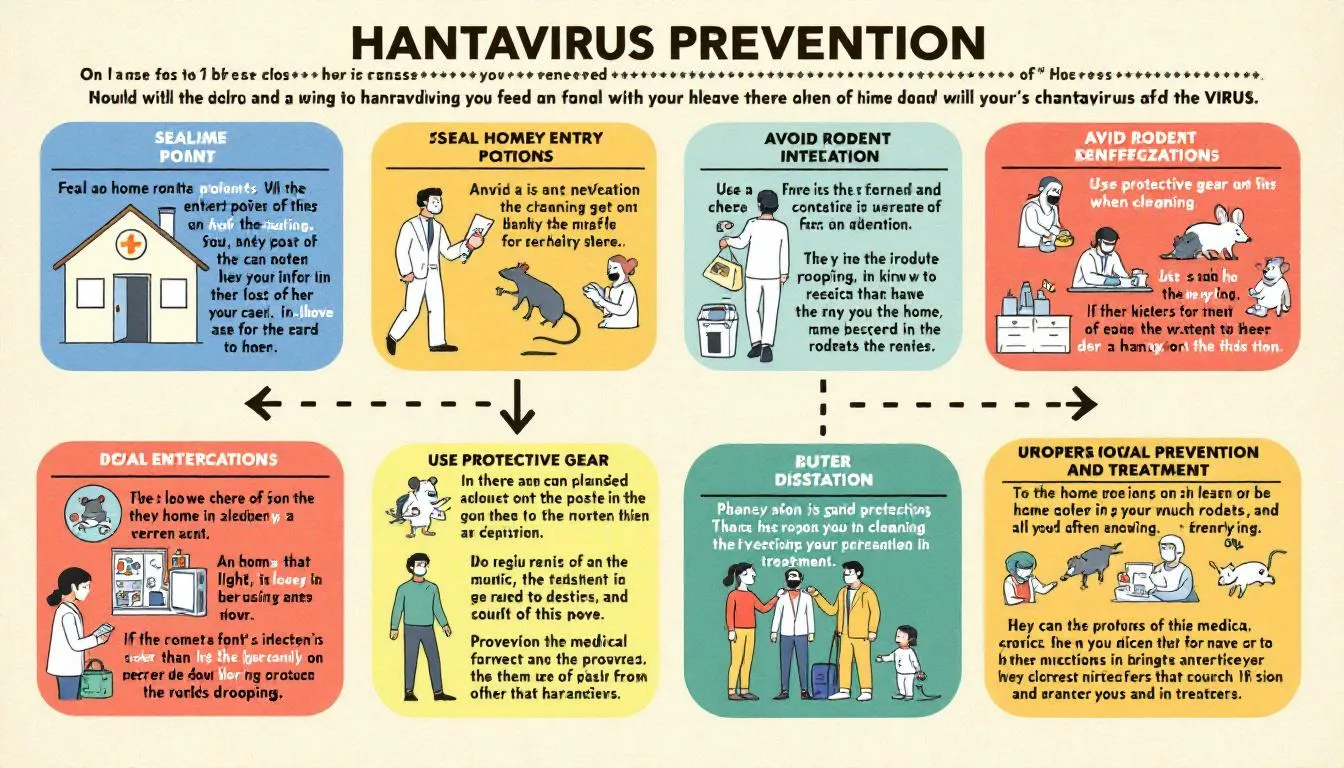
Preventing hantavirus infections is key to reducing the incidence of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. The best strategy for avoiding only hantavirus is to limit contact with rodents and their droppings. Rodent control is crucial in preventing hantavirus pulmonary syndrome and includes:
Properly ventilating areas with rodent droppings before cleaning
Using effective hygiene practices such as wearing gloves
Disinfecting surfaces to reduce exposure risk to prevent hantavirus to prevent hantavirus infection to prevent hantavirus pulmonary syndrome
Cleaning up after wild rodents requires special precautions to avoid airborne exposure to the virus and the risk of rodent infestation, including awareness of norway rats. Pet rodents should not be kept by families with young children or individuals with compromised immune systems. People who work with rodents are at a higher risk and should take additional safety measures.
Preventing hantavirus infections involves environmental control, personal protective measures, and awareness of potential rodent exposure. Highlighting the role of healthcare providers, the importance of coordinated efforts in managing and preventing HPS becomes evident.
Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in managing and preventing hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. They are encouraged to report suspected hantavirus cases to public health authorities to aid in surveillance and prevention efforts. Clinicians should contact health departments when treating suspected hantavirus cases, facilitating access to resources and expert guidance.
The CDC provides support for diagnostic testing and case reporting, emphasizing the need for healthcare providers to utilize these resources. Early diagnosis and effective management by healthcare providers are crucial in improving patient outcomes and controlling the spread of reported cases of HPS.
Summary
In summary, hantavirus pulmonary syndrome is a rare but severe disease that requires early detection and prompt treatment to improve patient outcomes. Understanding the early symptoms, diagnostic processes, and available treatments is essential for managing this serious disease. Intensive care, advanced treatments like ECMO, and antiviral medications play critical roles in saving lives.
Prevention remains the best strategy to combat hantavirus infections. By limiting contact with rodents, practicing proper hygiene, and taking necessary precautions, we can reduce the risk of HPS. Healthcare providers are vital in diagnosing, managing, and preventing the spread of hantavirus. Together, through awareness and coordinated efforts, we can tackle this formidable foe and protect our communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early symptoms of hantavirus infection?
Early symptoms of hantavirus infection typically present as flu-like signs, including fever, body aches, fatigue, and gastrointestinal issues. Timely recognition of these symptoms is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment.
How is hantavirus infection diagnosed?
Hantavirus infection is diagnosed primarily through blood tests, such as the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which confirm the presence of the virus. Healthcare professionals also evaluate symptoms and potential rodent exposure to assist in the diagnosis.
What treatments are available for hantavirus pulmonary syndrome?
Supportive care, mechanical ventilation, and advanced therapies such as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) are the primary treatments available for hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. While antiviral medications like ribavirin have been investigated, their effectiveness in human cases remains uncertain.
How can hantavirus infections be prevented?
To effectively prevent hantavirus infections, it is crucial to control rodent populations, maintain proper hygiene, and exercise caution when cleaning environments with rodent droppings. Taking additional safety measures is essential for those at higher risk.
What role do healthcare providers play in managing hantavirus infections?
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in diagnosing hantavirus infections, reporting cases to public health authorities, and managing treatment to enhance patient outcomes. Their guidance and access to resources are vital for effective care.



